Autoimmunity Research Foundation is a California-based 501(c)3. We study the molecular mechanisms by which persistent infection, microbiome dysbiosis, and the human exposome contribute to autoimmune disease and other chronic inflammatory conditions. We value patient-reported feedback and transition our research from bench to bedside in a proactive and transparent fashion.
Our Latest Publications
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in the Era of the Human Microbiome: Persistent Pathogens Drive Chronic Symptoms by Interfering With Host Metabolism, Gene Expression, and Immunity
The illness ME/CFS has been repeatedly tied to infectious agents such as Epstein Barr Virus. Expanding research on the human microbiome now allows ME/CFS-associated pathogens to be studied as interacting members of human microbiome communities. Humans harbor these vast ecosystems of bacteria, viruses and fungi in nearly all tissue and blood. Most well-studied inflammatory conditions are tied to dysbiosis or imbalance of the human microbiome. While gut microbiome dysbiosis has been identified in ME/CFS, microbes and viruses outside the gut can also contribute to the illness. Pathobionts, and their associated proteins/metabolites, often control human… (read full paper)
Re-framing the Theory of Autoimmunity in the Era of the Microbiome: Persistent Pathogens, Autoantibodies, and Molecular Mimicry
The theory of autoimmunity was developed at a time when the human body was regarded as largely sterile. Antibodies in patients with chronic inflammatory disease could consequently not be tied to persistent human pathogens. The concept of the “autoantibody” was created to reconcile this phenomenon. Today, however, the discovery of the human microbiome has revolutionized our understanding of human biology. Humans are superorganisms that harbor trillions of persistent microbial cells. Indeed, vast human microbiomes have been detected in human tissue and blood. These microbial ecosystems harbor thousands of newly identified bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms — most of which can act… (read full paper)

Microbe-Microbe and Host-Microbe Interactions Drive Microbiome Dysbiosis and Inflammatory Processes
An extensive microbiome comprised of bacteria, viruses, bacteriophages, and fungi is now understood to persist in nearly every human body site, including tissue and blood. The genomes of these microbes continually interact with the human genome in order to regulate host metabolism. Many components of this microbiome are capable of both commensal and pathogenic activity. They are additionally able to persist in both “acute” and chronic forms. Inflammatory conditions historically studied separately (autoimmune, neurological and malignant) are now repeatedly tied to a common trend: imbalance or dysbiosis of these microbial ecosystems. Population-based studies of the microbiome can shed light… (read full paper)
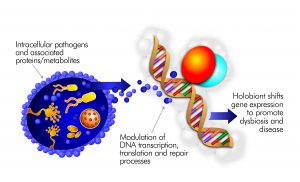
Inflammatory Disease and the Human Microbiome
The human body is a superorganism in which thousands of microbial genomes continually interact with the human genome. A range of physical and neurological inflammatory diseases are now associated with shifts in microbiome composition. Seemingly disparate inflammatory conditions may arise from similar disruption of microbiome homeostasis. Intracellular pathogens long associated with inflammatory disease are able to slow the innate immune response by dysregulating activity of the VDR nuclear receptor. This facilitates the ability of other species to gradually accumulate in tissue and blood, where they generate proteins and metabolites that significantly interfere with the body’s metabolic processes. The microbes that… (read full paper)
